World Food Safety Day
Journal link:
https://www.mdpi.com/journal/foods
Wechat link:
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s? __biz=MzI1MzEzNjgxMQ==&mid=2650002090&idx=4&sn=
2b66382978c4dc7d63d665ad4228f5bd&chksm=f1de686ec6a9e178feb775660d1634b5
9dc55dffb3b3c6bd88a841790fcadc9db97687c0cb6e&token=2105563179&lang=zh_CN#rd
As the saying goes, "If you want to be healthy, food should be fresh", food safety has always been our top priority. June 7th is the World Food Safety Day designated by the United Nations, which aims to draw people’s attention to food safety, encourage people to take actions to help prevent, detect and manage food-borne risks, and make contributions to food security, human health, economic prosperity, agricultural development, market access, tourism and sustainable development.
This issue featured five articles published in 2021.FoodsExcellent articles in journals cover all aspects of the food field, from the perspective of food preservation, processing, microorganisms to consumers, which will have an important impact on food quality and safe production. Welcome to read and download.
1. Assessed versus Perceived Risks: Innovative Communications in Agri-Food Supply Chains
Assessing and Perceiving Risk: Innovative Communication in Agricultural Food Supply Chain
Fabio G. Santeramo et al.
DOI:10.3390/foods10051001
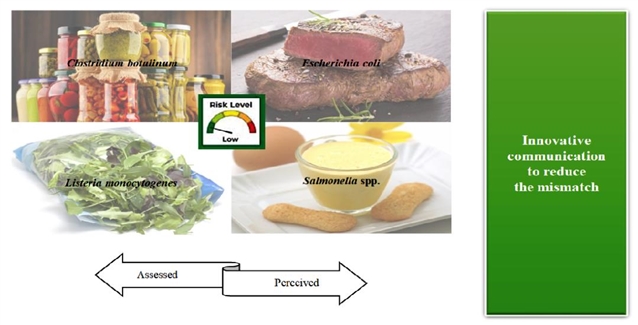
The picture shows the common foodborne pathogens in food preparation.
Food preparation is often criticized by people, especially those based on animal products, which is the reason for the increase of food-borne infections and also intensifies the pressure on the health care system. Risk assessment in agricultural food supply chain is very important for food industry and policy makers. Wrong risk cognition may change the operation of supply chain, so we should devote ourselves to more effective ways to pass risks. The author uses a multidisciplinary approach to investigate how consumers view different food risks. This study shows that it is very important to plan effective communication strategies to inform consumers of food risks. The potential innovation methods are discussed to better organize the supply chain.
2. From Cheese-Making to Consumption: Exploring the Microbial Safety of Cheeses through Predictive Microbiology Models
From cheese making to consumption: exploring the microbial safety of cheese through microbial prediction model
Arícia Possas, Olga María Bonilla-Luque and Antonio Valero
DOI:10.3390/foods10020355
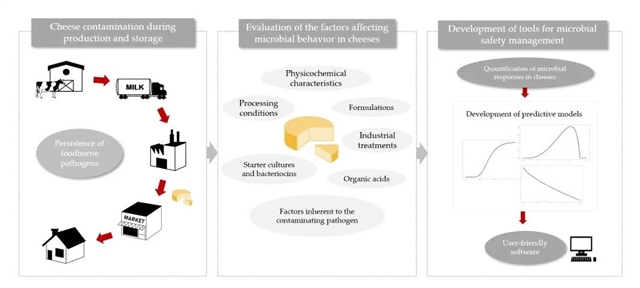
The picture shows microbial contamination, evaluation factors and prediction model during cheese making.
Cheese is a traditional product widely consumed all over the world, but it is usually related to food-borne diseases. The purpose of this study is to summarize and discuss the modeling methods available in cheese, and to determine the main microbial targets and the factors affecting microbial behavior in these products. In modeling research, Listeria is often used as the main pathogen for hazard assessment. The main factors such as pH value, water activity, lactic acid concentration and temperature are usually considered as independent variables in the model. Affected by different production processes, storage conditions and physical and chemical characteristics, microorganisms may grow or die in the process of cheese making. Classical two-step modeling is the most commonly used method to develop forecasting models. In addition, it also includes other modeling methods, microbial interaction, growth boundary, response surface method and neural network. The verified model has been integrated into user-friendly software tools to obtain the estimated value of microbial behavior in a fast and simple way. Future research should investigate the fate of other target bacterial pathogens (such as spore-producing bacteria) and the dynamic characteristics of cheese production process. The information collected in this study is helpful to deepen the knowledge of predictive microbiology under the background of cheese production and storage.
3. Fermentative Foods: Microbiology, Biochemistry, Potential Human Health Benefits and Public Health Issues
Fermented food: microbiology, biochemistry, potential human health benefits and public health problems
Chrysa Voidarou et al.
DOI:10.3390/foods10010069

The picture shows the microbial diversity in fermented food and its beneficial effects.
Fermented food is a symbol of culture and civilization. The particularity of history, climate and local raw material production urges human beings to explore various fermentation ways to produce various traditional edible products, which represent the adaptation to specific conditions. At present, the global fermented food market is close to 30 billion dollars, and it is still on the rise. Therefore, fermented foods are facing two major challenges at present. One is the safety of hand-fermented products, which can be solved by molecular biology, involving not only the existence of pathogens, but also the drug resistance of food-borne microorganisms. In this review, the author discusses the microbial diversity of fermented food during fermentation and its influence on human health. In addition, the safety of fermented food has also attracted much attention. From Hippocrates to modern disease treatment methods, diet is considered to be the most important factor for the health and stability of human natural microorganisms. After all, to quote Pasteur, "Gentlemen, microorganisms are the final word of human health." In this sense, the microflora in fermented food will play a leading role in nutrition and treatment in the future.
4. A Review into the Effectiveness of Ozone Technology for Improving the Safety and Preserving the Quality of Fresh-Cut Fruits and Vegetables
Study on the effectiveness of ozone technology in improving the safety and preservation of fresh fruits and vegetables
Rinaldo Botondi, Marco Barone and Claudia Grasso
DOI:10.3390/foods10040748
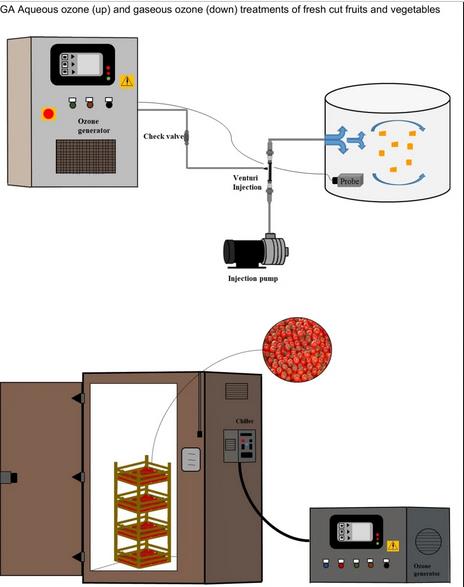
The picture shows the water-phase ozone treatment (I) and gaseous ozone treatment (II) of fresh-cut fruits and vegetables.
In recent years, more and more consumers realize that eating fresh fruits and vegetables regularly can reduce the risks of health and disease. Therefore, high-quality raw materials are essential, because the products that have undergone the simplest processing are easy to rot and easily lead to quality degradation. The process of cutting, peeling, cleaning and packaging of plant tissue surface and biochemical, sensory and microbial changes may accelerate deterioration. The main reason for the deterioration of raw materials is biological pollution, and ozone technology is an efficient sterilization technology that can be used to extend the shelf life of fresh-cut products. In this paper, the effects of ozone and ozone water treatment on microbial growth and quality maintenance of fresh-cut fruits and vegetables were studied. The purpose is to expand our understanding of environmental protection technologies, such as ozone technology, which can prolong shelf life, maintain the quality of fresh agricultural products, and will not emit harmful chemicals, which will have a negative impact on plant materials and the environment.
5. Histamine Control in Raw and Processed Tuna: A Rapid Tool Based on NIR Spectroscopy
Histamine control in tuna fresh-keeping and processing: a rapid tool based on near infrared spectroscopy
Sergio Ghidini et al.
DOI:10.3390/foods10040885

Fig. is a flow chart of a near infrared spectral model for predicting histamine concentration in tuna raw materials and processed samples.
In this study, near infrared spectroscopy (NIR) analysis was carried out with the minimum sample size to explore whether it can be used as a feasible technology for rapid detection of histamine levels in raw fish and processed tuna. By establishing an orthogonal partial least squares regression (OPLSR) correction model, the histamine in artificially polluted fish was predicted by using the near infrared spectrum of 1000-2500 nm, and the prediction range was 10-1000 mg kg.− one. Then, a new set of natural pollution samples was used as a control to verify the two models, and the histamine content was determined by traditional high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) analysis. Both models are in the verification stage, R.2Value > 0.97, RMSEP) ≤ 10 mg kg− one, relative range error (RER) ≥ 25. The prediction effect of the processed fish model is good. The results show that near infrared spectroscopy can be used as an effective analytical method for the determination of histamine content in fishery and market.
Brief introduction of periodicals
Foods (ISSN 2304-8158,IF 4.092As an open access international journal, it mainly publishes relevant papers in the field of food research. Its subject areas include: food science and technology, physical and chemical properties of food, food safety, food microbiology, functional food and health. At present, it has been included in Scopus, SCIE (Web of Science), PubMed and other databases.Foods Single blind peer review is adopted, and the average period of first instance is about14God, the article only needs to be received and published.fourGod.

